You can sign into Office 365 to download and install Office on your MAC or PC.
Note: Your account needs to be assigned a license that includes Office products in order to download and install.
Sign in to download Office for PC
-
Go to https://portal.office.com and if you're not already signed in, select Sign in.
-
Sign in with the account you associated with this version of Office.
-
After signing in, follow the steps:
-
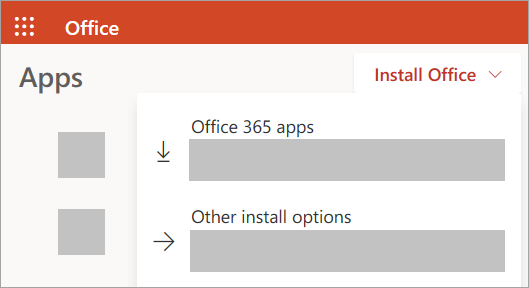
From the Office 365 home page select Install Office apps
-
Select Office 365 apps to begin the installation.
Note: The 64-bit version is installed by default unless Office detects you already have a 32-bit version of Office (or a stand-alone Office app such as Project or Visio) installed. In this case, the 32-bit version of Office will be installed instead.
To change from a 32-bit version to a 64-bit version or vice versa, you need to uninstall Office first (including any stand-alone Office apps you have such as Project of Visio). Once the uninstall is complete, sign in again and select Other install options, choose the language and version you want (64 or 32-bit), and then select Install. -
-
This completes the download of Office to your device. To complete the installation, follow the prompts in the "Install Office" section below.
Install Office
-
Depending on your browser, select Run (in Edge or Internet Explorer), Setup (in Chrome), or Save File (in Firefox).
If you see the User Account Control prompt that says, Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device? select Yes.
The install begins.

-
Your install is finished when you see the phrase, "You're all set! Office is installed now" and an animation plays to show you where to find Office applications on your computer. Select Close.

Activate Office
-
To open an Office app, select the Start button (lower-left corner of your screen) and type the name of an Office app, like Word.
If you have Windows 8.1 or 8.0, type the name of an Office app on the Start screen.
-
To open the Office app, select its icon in the search results.
-
When the Office app opens, accept the license agreement. Office is activated and ready to use.
Note: The Activation Wizard appears if Office has trouble activating. Complete the steps in the wizard to finish activating Office.
Install Office for Mac
-
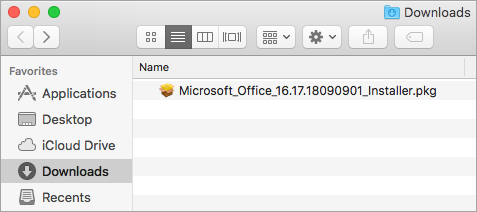
Once the download has completed, open Finder, go to Downloads, and double-click Microsoft Office installer.pkg file (the name might vary slightly).
Tip: If you see an error that says the Microsoft Office installer.pkg can't be opened because it is from an unidentified developer, wait 10 seconds and move the downloaded file to your desktop. Hold Control + click the file to launch the installer.
-
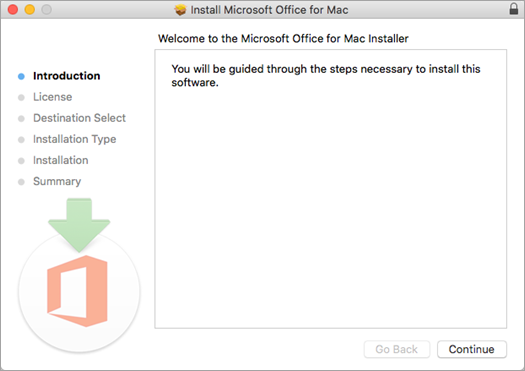
On the first installation screen, select Continue to begin the installation process.
-
Review the software license agreement, and then click Continue.
-
Select Agree to agree to the terms of the software license agreement.
-
Choose how you want to install Office and click Continue.
-
Review the disk space requirements or change your install location, and then click Install.
Note: If you want to only install specific Office apps and not the entire suite, click the Customize button and uncheck the programs you don't want.
-
Enter your Mac login password, if prompted, and then click Install Software. (This is the password that you use to log in to your Mac.)

-
The software begins to install. Click Close when the installation is finished.
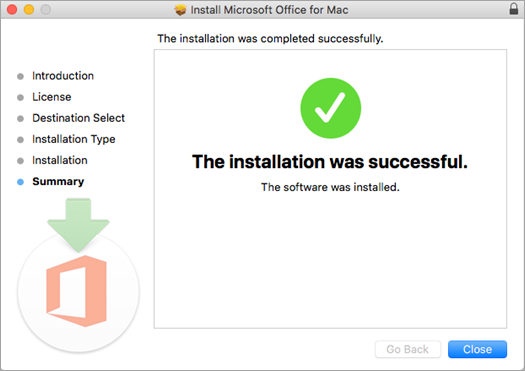
Launch an Office for Mac app and start the activation process
-
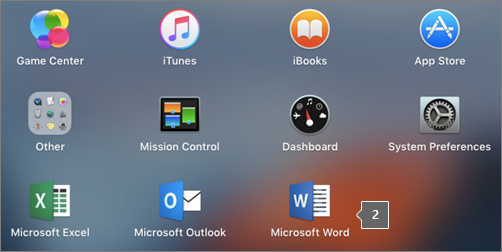
Click the Launchpad icon in the Dock to display all of your apps.

-
Click the Microsoft Word icon in the Launchpad.
-
The What's New window opens automatically when you launch Word. Click Get Started to start activating.